What is Mixed Reality?
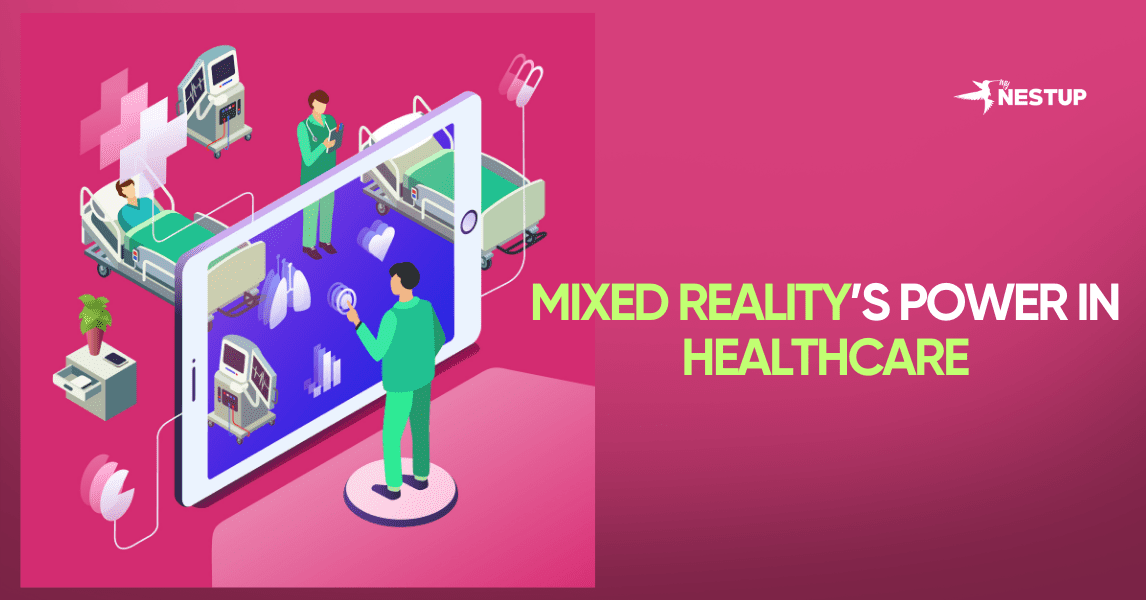
Mixed Reality (MR) is fundamentally changing healthcare by blending the real and digital worlds. It’s a game-changer for surgical training, allowing trainees to see 3D patient anatomy overlaid on the real world. This setup significantly improves planning and helps develop critical skills. The result is greater accuracy and fewer errors, leading to higher satisfaction among those being trained. Beyond training, MR acts as a powerful therapeutic tool for surgeons. It allows them to visualize complex structures, like a tumor or the liver’s internal anatomy, directly during an operation. This visualization aids in patient discussions and optimizes the surgical approach. Ultimately, using MR leads to better patient outcomes, quicker surgery times, and increased patient happiness.
Mixed Reality in Surgery: Key Applications
- Surgical Planning & Visualization: MR allows surgeons to use patient-specific data (from CT/MRI) to create 3D holographic overlays of anatomy, such as tumors or blood vessels, before the operation. This process helps them optimize the surgical strategy and anticipate challenges.
- Intraoperative Guidance: During the actual procedure, MR provides real-time guidance. The surgeon wears a headset that overlays critical patient data and the planned surgical path directly onto the patient’s body in their field of view. This enhances accuracy in delicate procedures like liver resections or tumor removals.
- Improved Patient Counseling: Surgeons can use MR models to show patients their specific anatomy and explain the planned procedure visually in 3D. This improves patient understanding and leads to increased patient satisfaction with the process.
- Enhanced Outcomes: By improving surgical visualization and precision, MR helps to reduce operating times and minimize surgical errors. The result is generally better clinical outcomes for the patient.
Mixed Reality for Surgical Guidance and Patient Care:
Mixed Reality (MR) is transforming surgery by providing real-time visualization that allows surgeons to effectively “see through” the patient’s surface, overlaying critical hidden structures like blood vessels or nerves and instruments directly onto the body to dramatically enhance precision. The technology significantly aids in preoperative planning, enabling surgeons to create highly detailed, risk-assessed strategies for complicated operations on organs like the liver or kidney. This advanced guidance leads to better surgical outcomes by improving accuracy, potentially reducing operation length, lowering the risk of converting procedures, and holding the potential to reduce general medical errors. MR plays an important role in patient engagement, as surgeons can use the 3D MR models to clearly explain complex procedures, fostering better understanding and increasing patient satisfaction.
Scope and Usage of Mixed Reality in Healthcare:
Mixed Reality (MR) has four main applications in healthcare. Intraoperative Guidance is a key use; it provides real-time navigation during surgery. It overlays 3D patient data from scans like CT or MRI directly onto the patient’s body. This gives surgeons precise guidance and minimizes the need to look at external monitors, boosting efficiency and safety. For Education and Training, MR offers highly immersive learning. Trainees practice procedures in safe, realistic, and repeatable simulated environments. This flattens the learning curve and significantly builds confidence. In Therapy and Rehabilitation, MR provides engaging, gamified environments. These are used for physical therapy and are also effective in mental health treatments like exposure therapy. MR enables crucial Remote Collaboration. Specialists can offer real-time, expert guidance to local surgical teams. This delivers specialized assistance to remote or underserved locations worldwide.
Conclusion:
Mixed Reality (MR) is fundamentally revolutionizing healthcare. It achieves this by seamlessly blending digital information with the real world. This capability is vital for both surgical guidance and training. MR improves precision by allowing surgeons to visualize hidden anatomy in real-time. It also enables detailed preoperative planning for complex cases. Beyond the operating room, MR offers immersive education for trainees and engaging therapy for patients. It facilitates expert remote collaboration across the globe. MR enhances surgical outcomes, improves patient understanding, and increases efficiency across the entire clinical workflow.
References:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/mixed-reality/discover/mixed-reality
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/computer-science/mixed-reality