What is a Sustainable Product?
A sustainable product is one that is produced and used in ways that limit negative and social impact and remain economically practical. It focuses on using resources efficiently (such as energy, water, raw materials) and in a way that natural systems are not depleted or damaged. Sustainable products are often made from renewable, recycled, or responsibly sourced materials. They are designed to last longer and have a lower carbon footprint.
From a social perspective, sustainable products consider fair labor practices and safe working throughout the supply chain. Economically, they aim to deliver long-term value by reducing costs and supporting circular economy practices like repair, reuse, and recycling.
The mission behind sustainable product development is rooted in the idea of meeting present needs without compromising future generations. This means ensuring that the environment retains its ability to provide resources while supporting economic growth and human development in a responsible way.
Examples:
Here are a few everyday examples of sustainable products:
– Clothes made from eco-friendly fabrics like organic cotton or bamboo.
– Furniture built from recycled or reclaimed wood.
– Electronics designed with recycled materials and energy-efficient parts.
– Renewable energy options, such as solar panels or wind power.
– Green building materials, like low-VOC paints or insulation made from recycled content.
– Products created through fair-trade or ethically sourced supply chains.
– And in general, anything that uses natural resources responsibly and cuts down on waste.

Why Sustainable Product Use Matters?
The products we use every day have a bigger environmental impact than we realize. From the energy used to make them to the waste they leave behind once we are done with them. This growing impact is why sustainability has become so important.
- Climate Change
Industries, transportation and energy production release large amounts of greenhouse gases. It leads to rising sea levels and extreme weather. When businesses choose renewable energy and energy-efficient designs, they can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and support global efforts to slow climate change. - Resource Depletion
We are using natural resources such as fossil fuels and minerals, faster than nature can replace them. This overuse damages environment and puts future resource availability at risk. Shifting to renewable resources helps ease the pressure on these limited supplies. - Pollution and Waste
Single-use plastics, overflowing landfills, and toxic electronic waste all pose serious environmental and health threats. Sustainable product design focuses on reducing waste by using recyclable materials, biodegradable components, and closed-loop systems that keep materials in use and out of the environment.
Benefits of Sustainable Products:
- Economic Benefits: Sustainable products can actually save businesses money over time because they usually use fewer raw materials and less energy. They also tend to appeal more to customers, giving companies a strong competitive edge.
- Environmental Impact: By using fewer natural resources, creating less waste, and cutting down on pollution, sustainable products have a much smaller environmental footprint compared to traditional alternatives.
- Social Benefits: Sustainable products can support job creation in underserved communities and encourage fair trade, helping resources and opportunities be shared more evenly around the world.
- Product Development: Designing with sustainability in mind often leads to more creative, efficient products. This not only improves customer satisfaction but can also boost sales.
- Sustainable Practices: When businesses commit to sustainable products, they reduce their environmental impact and position themselves as responsible, forward-thinking organizations.
Consumer Demand For Sustainable Products:
- Growing Awareness of Environmental Issues
Today’s consumers are much more aware of the impact of unsustainable practices. All thanks to constant media coverage and global advocacy. People want products that align with their values and do less harm to the planet. - Preference for Sustainable Brands
Brands that put sustainability at the center of their business for example Patagonia and IKEA, earn strong consumer trust. Their transparency and commitment to the environment make them favorites among eco-conscious shoppers who view their purchases as a statement of their values. - Willingness to Pay a Premium
More and more consumers are willing to spend extra on products that are ethically and sustainably produced. This shift gives businesses room to invest in greener technologies and innovative solutions without hurting profitability.

What is ESG?
ESG stands for environmental, social, and governance. It is basically a framework that helps measure how responsibly a company operates. Including how it treats the environment, how it supports people, and how well it managed. While it is often talked about in investing, ESG also matters to customers, employees, suppliers, and the community as a whole.
Three Main Pillars of ESG:
Environmental: This involves how a company takes care of the planet. It covers things like climate change, greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, biodiversity, carbon footprint, waste management, and pollution.
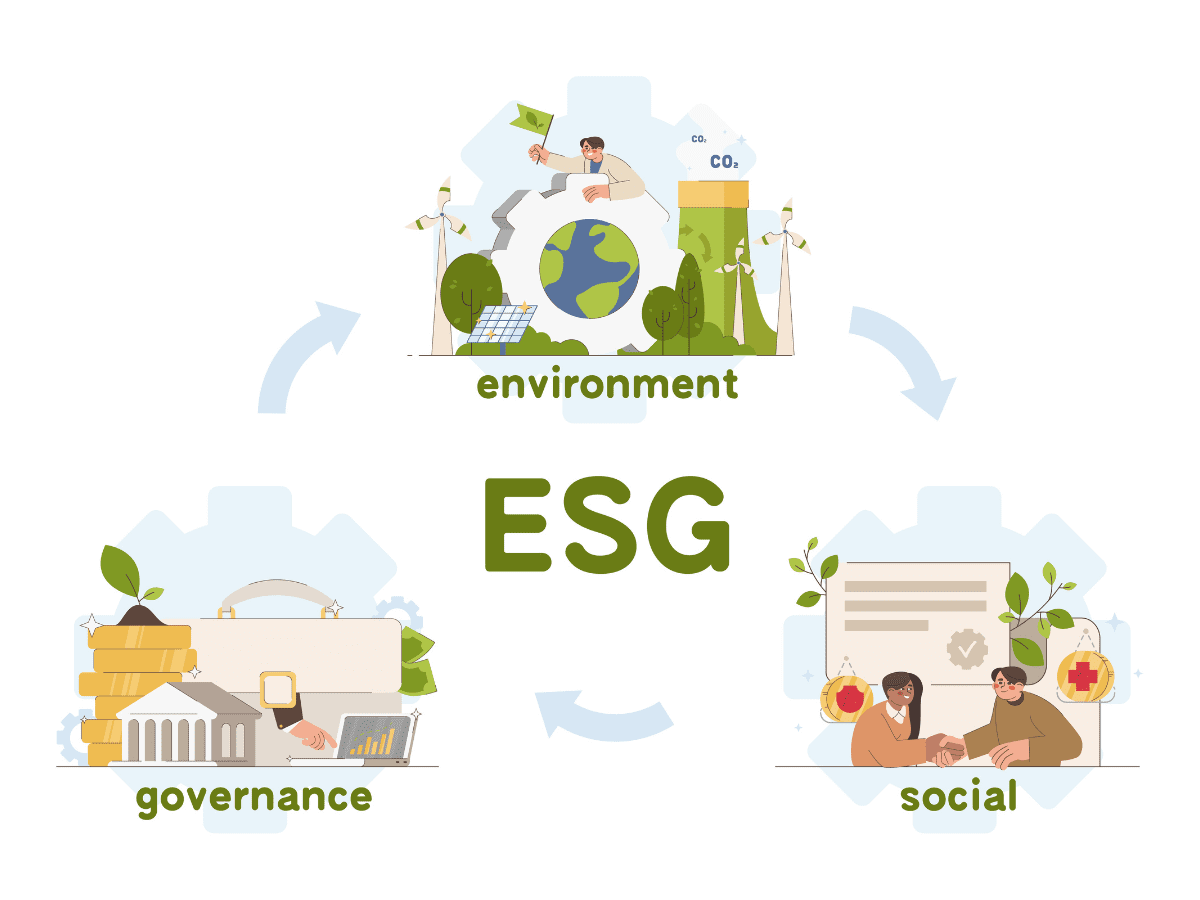
Social: This focuses on the company’s impact on people and communities. It considers diversity and inclusion, human rights, company’s relationships with employees, suppliers, and society at large.
Governance: This is about how a company is run. It includes things like executive pay, succession planning, board management, and protecting shareholder rights.
Benefits of ESG:
- Enhanced Reputation: When businesses set clear ESG goals and actually track their progress, it boosts their credibility. Customers and regulators tend to trust them more. This can translate into stronger loyalty and better investor confidence along with smoother relationships with authorities.
- Better Risk Management: Keeping an eye on ESG factors helps companies spot potential risks early whether financial, legal, or reputational. This makes it easier to address issues before they grow into bigger problems.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Good ESG practices often optimize operations. Cutting waste and using energy more efficiently can lower costs. For example, reducing energy use shrinks a company’s carbon footprint along with cutting down utility bills and boosts profitability.
- Cost Savings: Many ESG-focused changes pay off over time. Sourcing materials more sustainably and improving transportation can make supply chains cheaper and more efficient. Prioritizing worker health and safety also reduces the costs linked to injuries or illnesses.
- Stronger Employee Engagement: People want to work for companies that align with their values. When a business actively tracks and improves its ESG performance, it becomes more attractive to employees. This helps keep top talent and build a more motivated team.
- Greater Competitiveness: Companies that take ESG seriously often stand out in the market. As consumers and investors look for sustainable choices, strong ESG performance can become a real competitive edge.
- Improved Access to Capital: Investors are paying close attention to ESG performance. Companies that prioritize sustainability often find it easier to raise funds, sometimes at lower costs. It can result in long-term growth and profitability.
Sustainability and ESG:
ESG and sustainability are closely connected, but they are not the same thing. Both deal with environmental, social, and governance issues, however they differ in scope and purpose. ESG is more about measuring how well a company performs in these areas, while sustainability is a broader philosophy focused on running a business responsibly and ethically.
ESG is a set of standardized criteria used to assess a company’s impact on the environment, society and its own governance practices. Investors and stakeholders rely on ESG metrics to understand how a company manages issues like carbon emissions and diversity. Meanwhile sustainability, is a wider guiding principle. It is about making decisions that balance environmental health and economic stability. It focuses on long-term responsibility across areas like supply chain management and overall ethical practices.
The main difference is that ESG is a measurement tool, while sustainability is a holistic approach to doing business responsibly. ESG tells you how a company is performing in specific categories, whereas sustainability looks at the bigger picture of how the company operates and the impact it has on the world.

References:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-planetary-sciences/sustainable-product
https://www.arenasolutions.com/resources/glossary/sustainable-products
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sustainable_products
https://medium.com/@greenharmony/exploring-the-benefits-of-sustainable-products-1aea3a97fb68
https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/environmental-social-and-governance
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/e/environmental-social-and-governance-esg-criteria.asp